- Why Securonix?
- Products
-
- Overview
- 'Bring Your Own' Deployment Models
-
- Products
-
- Solutions
-
- Monitoring the Cloud
- Cloud Security Monitoring
- Gain visibility to detect and respond to cloud threats.
- Amazon Web Services
- Achieve faster response to threats across AWS.
- Google Cloud Platform
- Improve detection and response across GCP.
- Microsoft Azure
- Expand security monitoring across Azure services.
- Microsoft 365
- Benefit from detection and response on Office 365.
-
- Featured Use Case
- Insider Threat
- Monitor and mitigate malicious and negligent users.
- NDR
- Analyze network events to detect and respond to advanced threats.
- EMR Monitoring
- Increase patient data privacy and prevent data snooping.
- MITRE ATT&CK
- Align alerts and analytics to the MITRE ATT&CK framework.
-
- Industries
- Financial Services
- Healthcare
-
- Resources
- Partners
- Company
- Blog
Threat Research
Authors: Dheeraj Kumar, Ella Dragun
The Monthly Intelligence Insights provides a summary of top threats curated, monitored, and analyzed by Securonix Threat Labs in March. The report additionally provides a synopsis of the threats; indicators of compromise (IoCs); tactics, techniques, and procedures (TTPs); and related tags. This may be followed by a comprehensive threat summary from Threat Labs and search queries from the Threat Research team. For additional information on Threat Labs and related search queries used via Autonomous Threat Sweeper to detect the below mentioned threats, refer to our Threat Labs home page.
In March 2023, Threat Labs analyzed and monitored major threat categories, including multiple cyber campaigns involving attacks from APT groups originating from China, ChatGPT cyber campaign, and vulnerabilities seen from Telerik, Fortinet and Microsoft Office Outlook. Of note a suspected Chinese hacking group UNC3886 has been linked to a series of attacks on government organizations exploiting a Fortinet zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2022-41328) to deploy malware. FortiGate and FortiManager devices were compromised as well due to the connections to VIRTUALPITA from the Fortinet management IP addresses.
In March 2023, Securonix Autonomous Threat Sweeper identified 3,839 TTPs and IOCs, 122 distinct threats, and reported 36 threat detections. The top data sources swept against include IDS/IPS/UTM/Threat Detection, Endpoint Management Systems, Data Loss Prevention, and Email/Email Security.
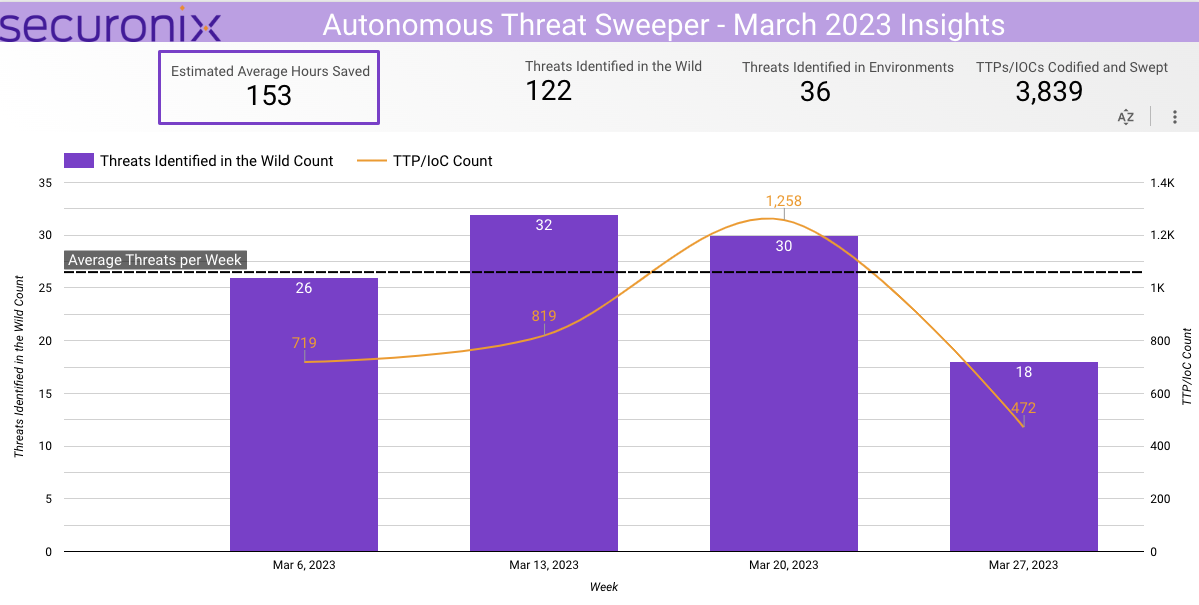
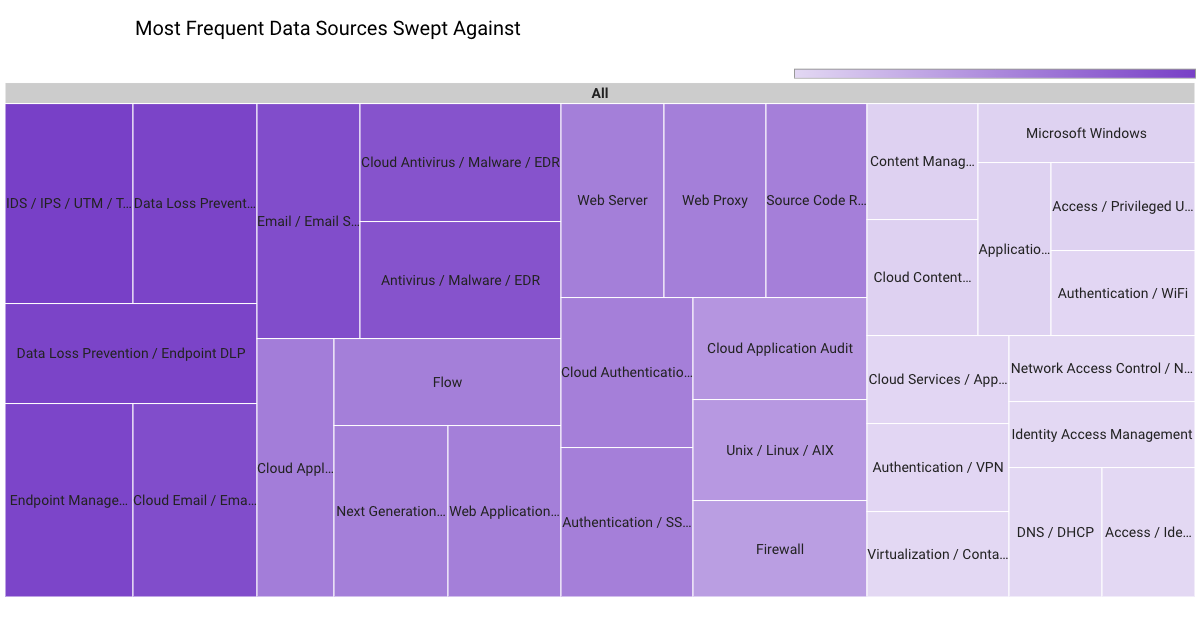
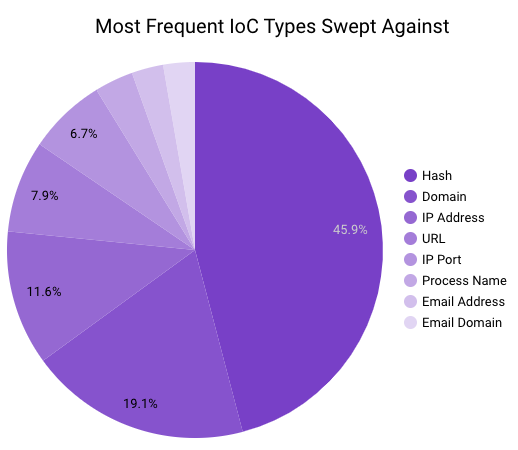
APT groups activity
(Originally published in March 2023)
Cyberespionage group APT27, also known as Iron Tiger, has created a new Linux version of its SysUpdate custom remote access malware, enabling more enterprise services to be targeted. In July 2022, hackers tested the Linux version for the first time. Nonetheless, multiple payloads were seen circulating in the wild only in October 2022. In addition to being written in C++, the new malware variant uses the Asio library, and is very similar to Iron Tiger’s SysUpdate for Windows. As with its Windows counterpart, SysUpdate on Linux is an ELF executable that shares common encryption keys and file-handling functions.
A new cyber-espionage campaign targeting governments and energy agencies in Commonwealth of Independent States (CIS) countries has been carried out by the threat actor named ‘YoroTrooper‘ since June 2022. Several European embassies, the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), and a key European Union healthcare agency have been compromised by the threat actor. YoroTrooper uses a number of tools, including commodity and custom information stealers, remote access trojans, and Python-based malware. The infection is transmitted via phishing emails containing decoy PDF documents and malicious LNK attachments. According to researchers, YoroTrooper exfiltrates large amounts of data from infected devices, including cookies and browsing history.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs is actively monitoring campaigns and has observed the following scenarios.
- A gambling company in the Philippines was one of the victims of the Iron Tiger campaign, which used a command and control server with a domain similar to the victims.
- The YoroTrooper group used corrupt PDF files to target Belarusian entities in the summer of 2022. It registered several typosquatting domains mimicking Russian government entities in September 2022. Threat actors used HTA to download decoy documents and dropper implants onto target systems by deploying a custom Python stealer against the governments of Tajikistan and Uzbekistan in 2023. Currently, malicious RAR and ZIP attachments are being used in phishing emails in connection with national strategy and diplomacy.
- 217 IOCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
Tags: Threat Actor: YoroTrooper, APT27, Iron Tiger | Target Sector: Government Organizations, Energy Organizations | Threat Actor Location: China | Target System: Linux
Exploitation of a security flaw in Fortinet FortiOS
(Originally published in March 2023)
In a CVSS Medium PSIRT Advisory related to the incident FG-IR-22-369 / CVE-2022-41328 published by Fortinet in March, FortiGate researchers identified that government entities and large organizations are targeted by an unknown threat actor exploiting a security flaw in Fortinet FortiOS software. Following data loss and OS and file corruption, multiple IOCs have been discovered. This exploit demonstrates an advanced actor specifically targeting governmental or government-related targets.
Affected products:
FortiOS version 7.2.0 through 7.2.3
FortiOS version 7.0.0 through 7.0.9
FortiOS version 6.4.0 through 6.4.11
FortiOS 6.2 all versions
FortiOS 6.0 all versions
Later this month, Mandiant researchers have discovered that a suspected Chinese hacking group UNC3886, has been linked to a series of attacks on government organizations exploiting a Fortinet zero-day vulnerability (CVE-2022-41328) to deploy malware.
It suspected the FortiGate and FortiManager devices were compromised as well due to the connections to VIRTUALPITA from the Fortinet management IP addresses. Additionally, the FortiGate devices with Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) compliance mode enabled failed to boot after it was later rebooted.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs is actively monitoring running campaigns by a suspected Chinese hacking group UNC3886 and other threat actors that are targeting government entities and large organizations.
- Threat Labs observed threat actors using access via the FortiManager device
- Threat Labs observed cyber espionage operators exploiting zero-day vulnerabilities and deploying custom malware to Internet-exposed systems as an initial attack vector.
- Threat Labs learned that the threat actor uses a local zero-day vulnerability in FortiOS (CVE-2022-41328) and deploys multiple custom malware families on Fortinet and VMware systems
- 37 IOCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers
Tags: Threat Actor: Chinese hacking group UNC388 | Target Sector: government entities and large organizations
ChatGPT cyber campaign
(Originally published in March 2023)
OpenAI Labs’ AI-powered chatbot ChatGPT rocketed to fame in just four months after it was launched. Sadly, fraudsters have taken advantage of the viral success of the AI tool to conduct sophisticated investment scams on unwary internet users.
Bitdefender confirmed that a phishing campaign uses a fake ChatGPT platform to swindle investors. At the moment, Denmark, Germany, Australia, Ireland, and the Netherlands are the target countries of the scheme.
In their analysis, researchers at G DATA have identified ChatGPT’s real doppelganger, chatgpt-go[.]online.
OpenAI’s ChatGPT can be accessed at openai.com/blog/chatgpt/ whereby users can try out artificial intelligence chatting with ChatGPT by clicking the TRY CHATGPT button that leads to the login and sign up page. However, users will see the same webpage on the fake website as they would on ChatGPT’s official site. Moreover, its website uses HTTPS to ensure that users are communicating securely with the website’s server by encrypting data traffic between their web browsers and the website’s server. Due to this, not every HTTPS-enabled website is automatically secure.
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs is actively monitoring running campaigns by threat actors / hackers that are targeting ChatGPT AIl.
- 7 IOCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
Tags: Campaign: Phishing | Target location: Denmark, Germany, Australia, Ireland, and Netherlands
Telerik vulnerability in U.S. government IIS server
(Originally published in March 2023)
In the past year, a .NET deserialization vulnerability in Progress Telerik UI for ASP.NET AJAX was exploited by hackers to hack into a U.S. federal agency’s Microsoft Internet Information Services (IIS) server.
CISA, FBI, and MS-ISAC issued a joint advisory reporting the attackers accessed the server between November 2022 and early January 2023 based on indicators of compromise (IoCs) on the unnamed federal civilian executive branch (FCEB) agency’s network.
It is believed that at least two threat actors (one of them the Vietnamese XE Group) exploited this bug CVE-2019-18935 (CVSS score: 9.8) to gain remote access to the unpatched server.
Hackers compromised the FCEB agency’s server and deployed malicious payloads in C:/Windows/Temp/ to collect data and transmit it to attacker-controlled command and control servers.
Threat Labs summary
- Threat Labs observed a threat actor tracked as Praying Mantis (aka TG2021) has also weaponized CVE-2019-18935, along with CVE-2017-11317, to infiltrate U.S. public and private networks.
- Securonix Threat Labs recommends testing the security program against MITRE ATT&CK techniques regularly in a production environment in order to achieve optimal performance.
- 94 IOCs are available on our Threat Labs home page repository and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
Tags: Vulnerability: CVE-2019-18935
Microsoft Office Outlook privilege escalation vulnerability
(Originally published in March 2023)
Microsoft has observed and announced a new high severity vulnerability with the code CVE-2023-23397 in Outlook for Windows that is being exploited to steal NTLM credentials. The company categorized it as a high CVSS score of 9.8, with CVSS being the evaluation score for the severity level. Researchers from ASEC have analyzed the Microsoft vulnerability in Outlook for Windows as well and confirms it is being exploited to steal NTLM credentials. This vulnerability affects all versions of Windows Outlook. CVE-2023-23397 is an elevation of privilege vulnerability in Microsoft Outlook. It is a zero-touch exploit that is a security gap that has low complexity and requires no user interaction. In most cases, the attacker sends a message to the victim with an extended Message Application Program Interface (MAPI) property with a Universal Naming Convention (UNC) path to a remote attacker-controlled Server Message Block (SMB, via TCP 445).
Threat Labs summary
Securonix Threat Labs recommends leveraging our findings to deploy protective measures for increased threats from this malware.
- Implement network segmentation and maintain offline backups of data to ensure limited interruption to your organization.
- Apply the vendor patches immediately. Microsoft has released a patch as part of their March 2023 Monthly Security Update.
- Block TCP 445/SMB outbound from your network.
- Customers can disable the WebClient service. Note that this will block all WebDAV connections, including intranet.
- Add users to the Protected Users Security Group.
- Enforce SMB sign on for clients and servers to prevent a relay attack.
- 28 IOCs are available on our Threat Labs home page and have been swept against Autonomous Threat Sweeper customers.
Tags: Vulnerability: Microsoft vulnerability CVE-2023-23397 in Outlook | Exploitation: steal NTLM credentials |Target areas: Government, transport, energy, and military sectors | Target location: Europe and Latin America.
For a full list of the search queries used on Autonomous Threat Sweeper for the threats detailed above, refer to our Threat Labs home page. The page also references a list of relevant policies used by threat actors.
We would like to hear from you. Please reach out to us at [email protected].
Note: The TTPs when used in silo are prone to false positives and noise and should ideally be combined with other indicators mentioned.
Contributors: Sina Chehreghani, Tim Johny







